- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
中国 アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカー、サプライヤー、工場
- View as
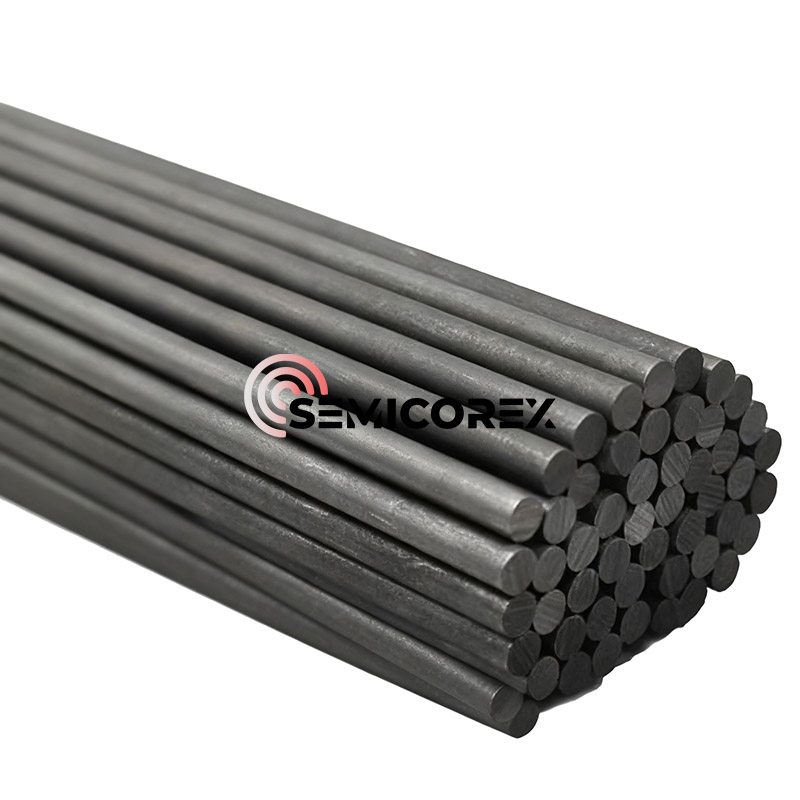
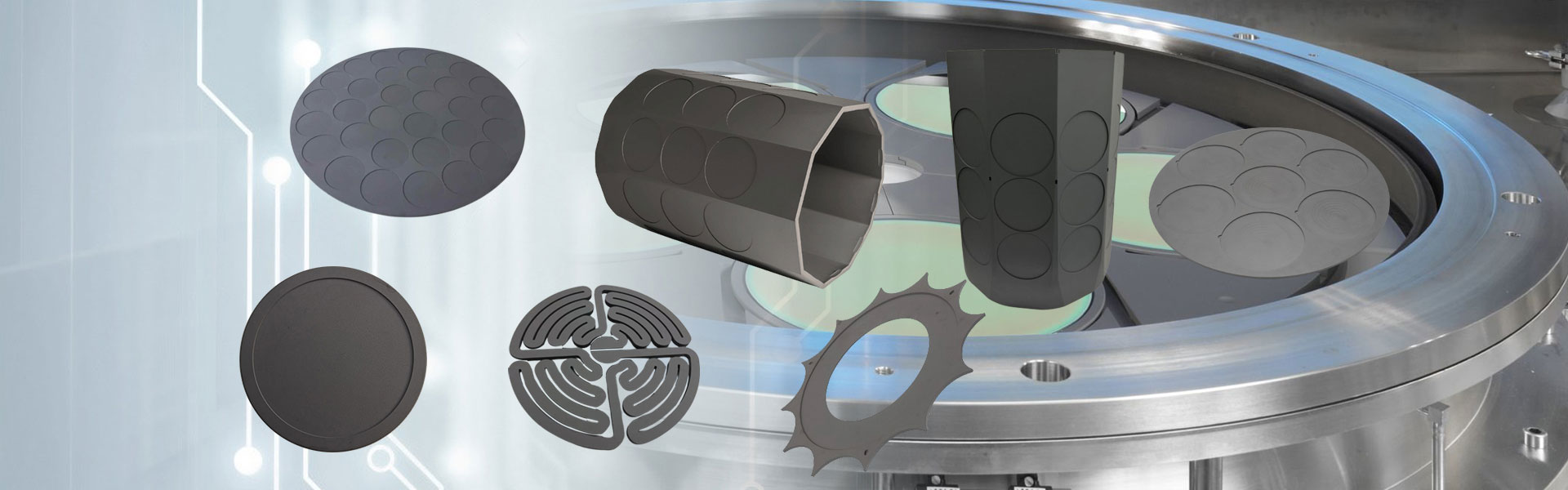
グラファイトチャック
Semicorex Graphite Chuckは、Polysilicon製造における重要なコンポーネントであり、太陽産業で広く使用されています。高純度のシリコンウェーハの需要が増加するにつれて、グラファイトチャックなどの高性能処理ツールの必要性が不可欠になりました。高純度の特殊グラファイトから製造されたグラファイトチャックは、寸法の安定性を維持しながら、極端な温度、化学物質への曝露、および機械的ストレスに耐えるように設計されています。*
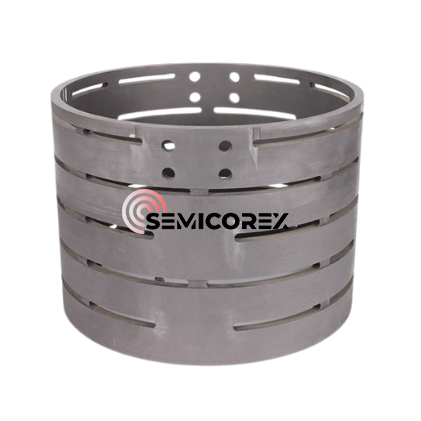
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信グラファイトローターとシャフト
Semicorex のグラファイト ローターとシャフトのアセンブリは、主にアルミニウムおよびアルミニウム合金の精錬における脱ガスに使用される重要な部品です。
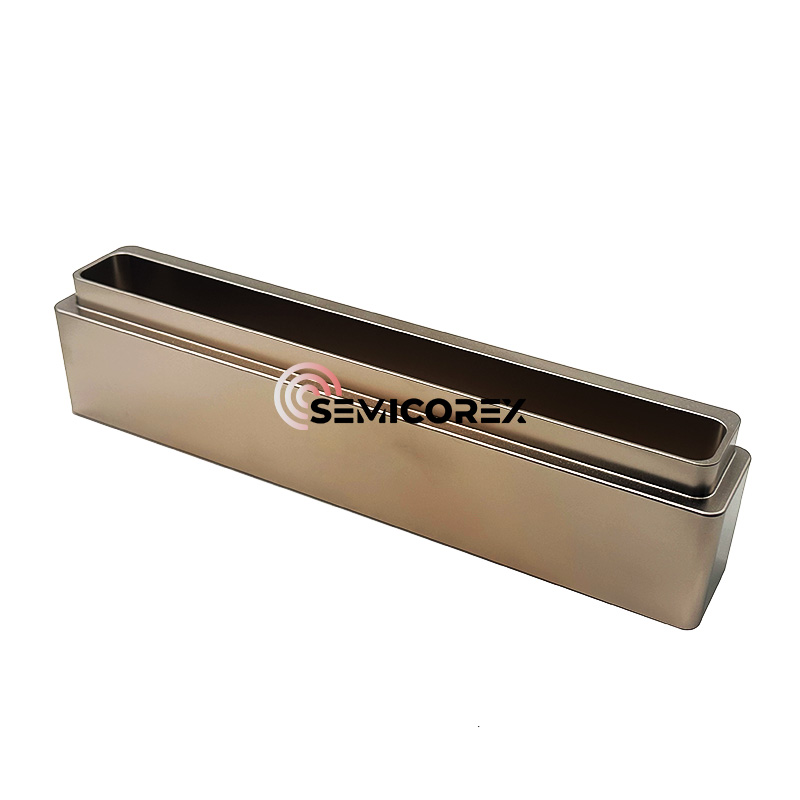
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信グラファイトヒートシールド
過酷な環境での処理効率を確保するために、Semicorex グラファイト ヒート シールドは、高級グラファイト素材と最先端の製造技術で作られています。
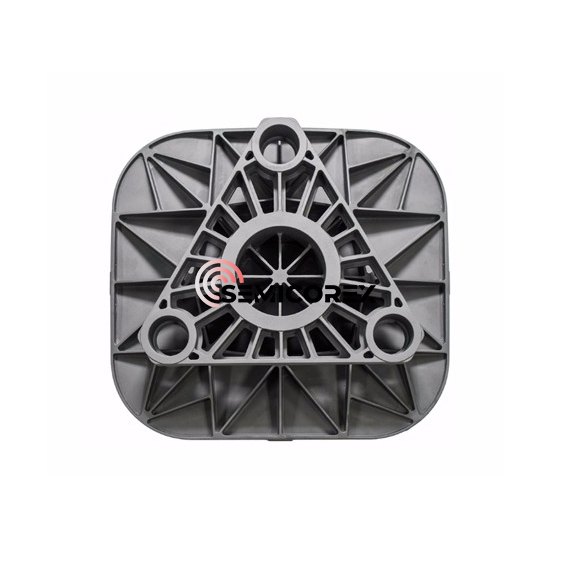
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信グラファイトブッシュ
Semicorex グラファイト ブッシングは、その独自の材料特性と適応性により、機械システムの性能と寿命を向上させる上で重要な役割を果たし、現代のエンジニアリングおよび製造プロセスにおけるその重要性を強調しています。
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信
Semicorex は アイソスタティックグラファイト を長年生産しており、中国のプロの アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカーおよびサプライヤーの 1 つです。バルク梱包を提供する高度で耐久性のある製品を購入すると、迅速な配達で大量の製品を保証します。長年にわたり、お客様にカスタマイズされたサービスを提供してきました。お客様は当社の製品と優れたサービスに満足しています。私たちはあなたの信頼できる長期的なビジネスパートナーになることを心から楽しみにしています!私たちの工場から製品を購入することを歓迎します。