- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
中国 アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカー、サプライヤー、工場
- View as
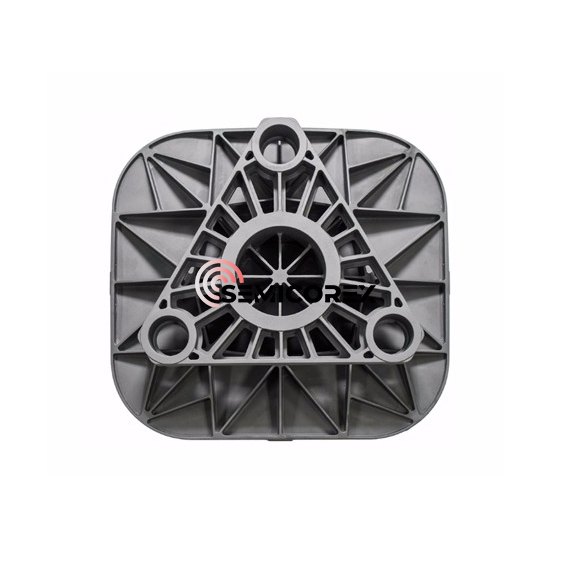
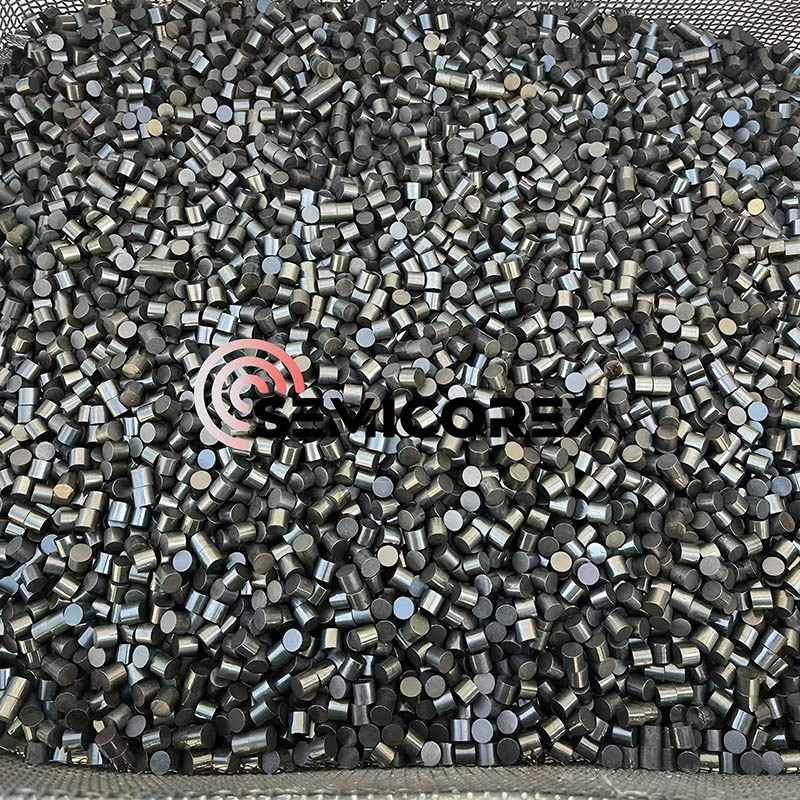
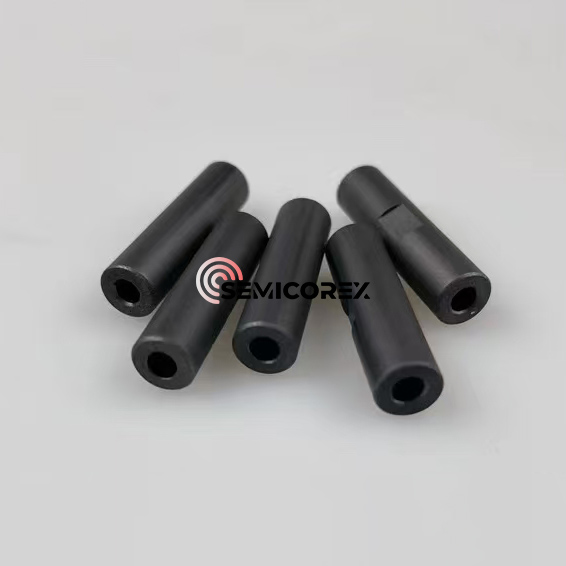
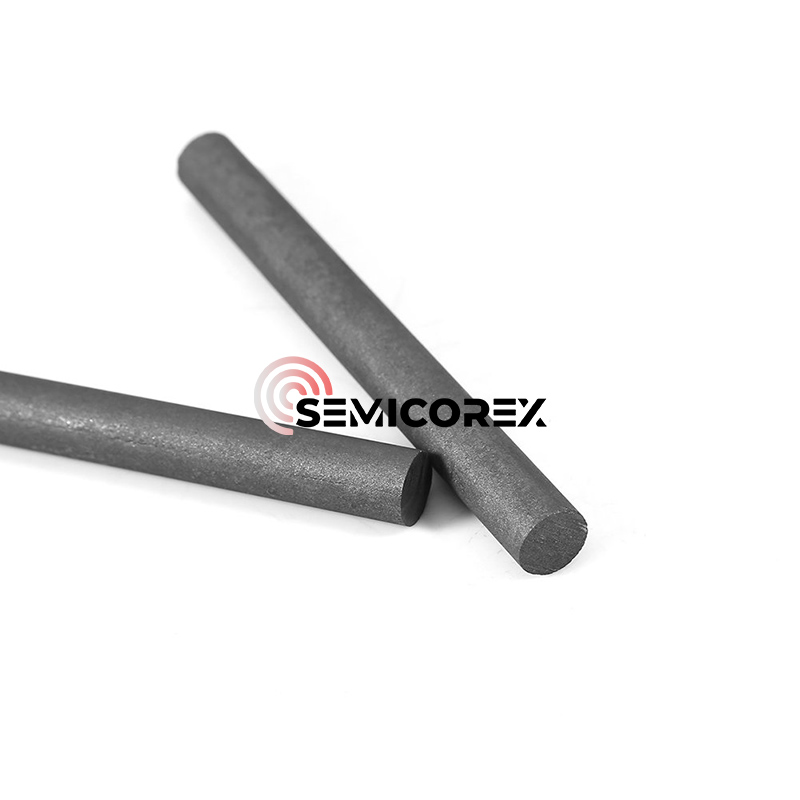
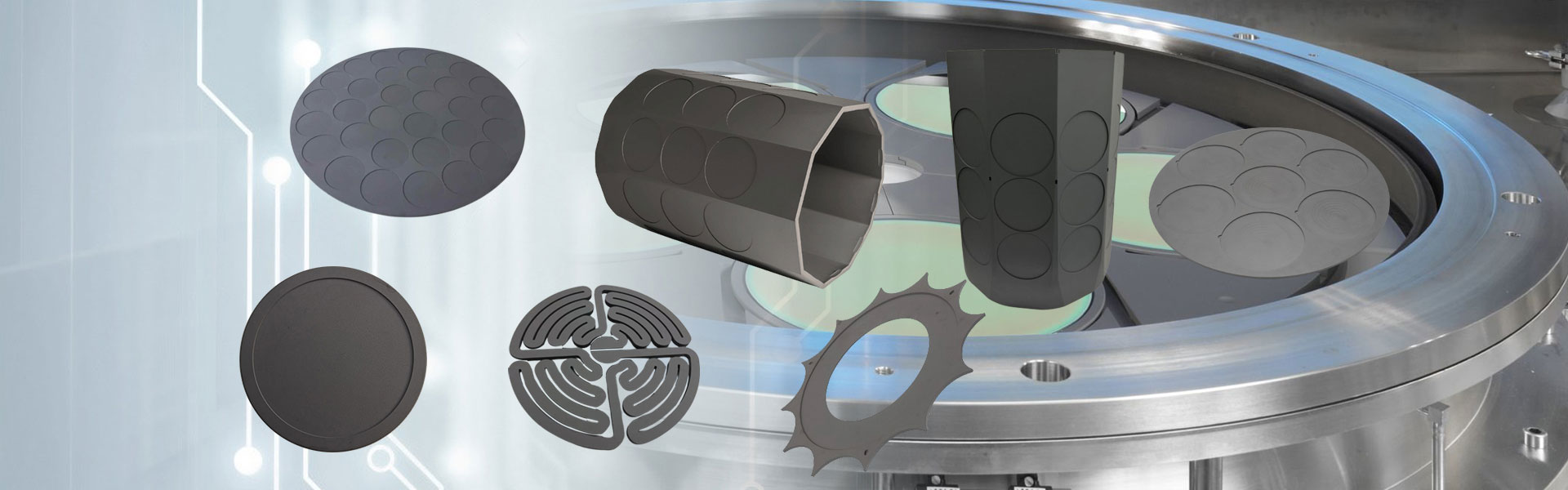
半導体グラファイトヒーター
Semicorex 半導体グラファイトヒーターは、高品質等方性グラファイトで作られた高効率加熱装置です。結晶成長炉の熱分野、エピタキシャル成長プロセス、イオン注入装置、プラズマエッチング装置、半導体デバイス焼結金型の製造など、半導体製造の中核プロセスリンクで広く使用されています。
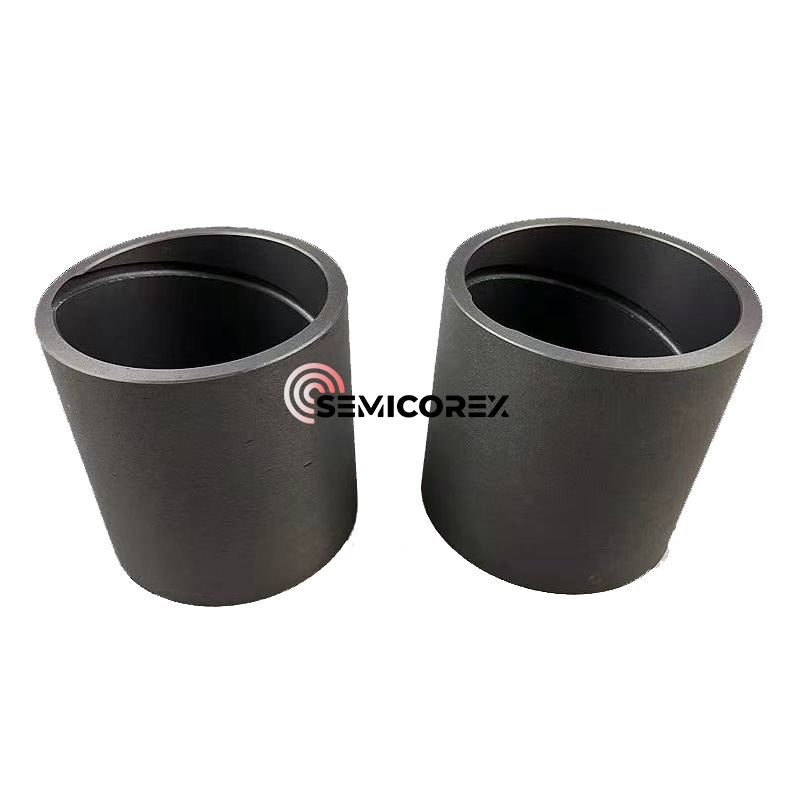
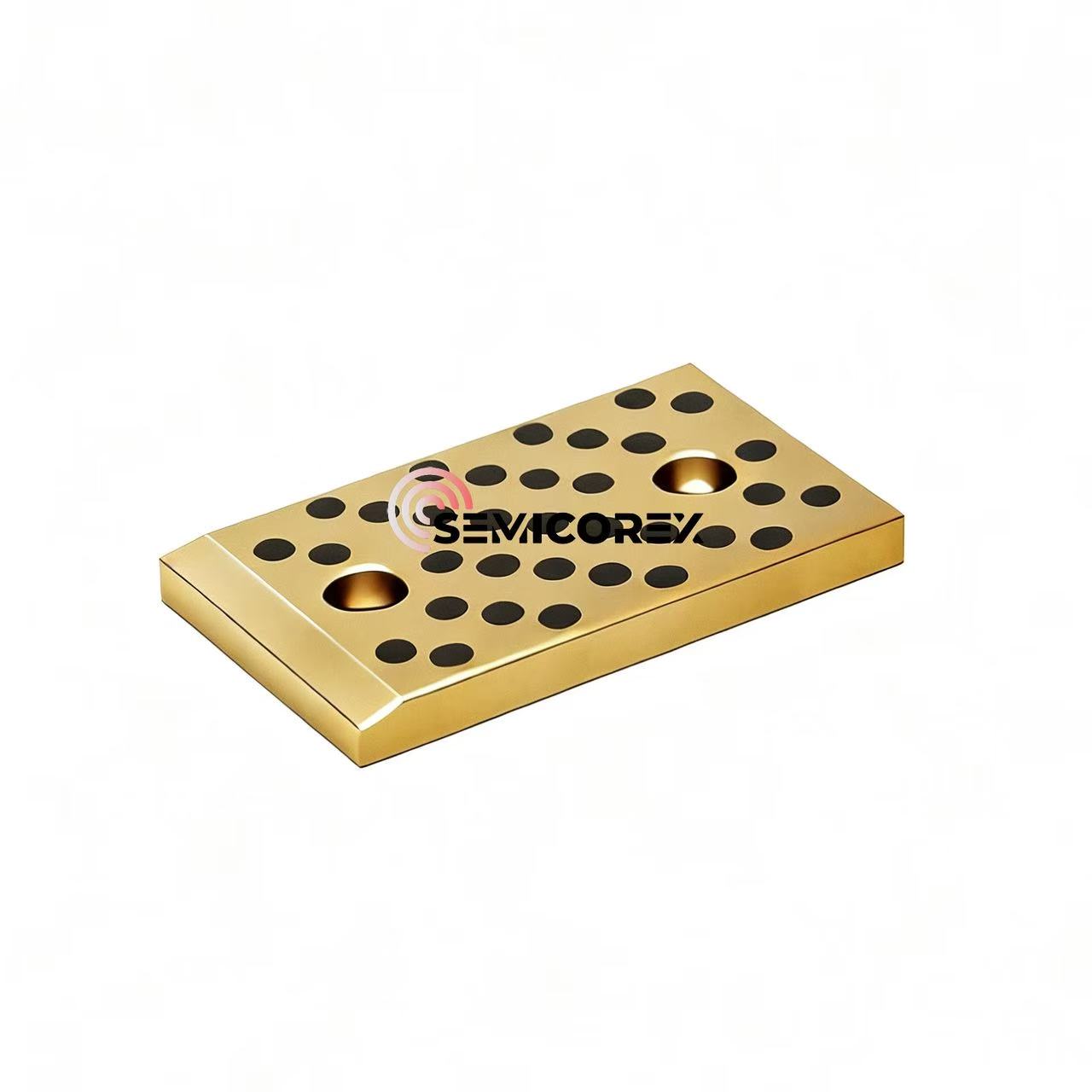
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信グラファイトスライドプレート
Semicorex のグラファイト スライド プレートは自己潤滑機能を備えており、機械的な走行抵抗を効果的に低減し、作業効率を向上させ、潤滑の不十分または失敗によって引き起こされる機械的故障を最小限に抑えることができます。
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信
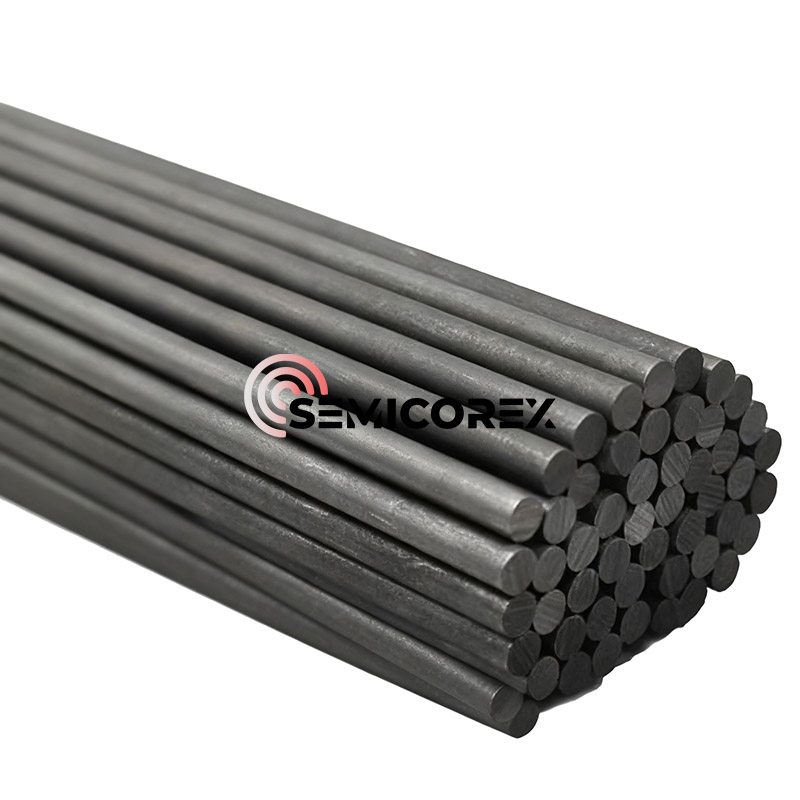
Semicorex は アイソスタティックグラファイト を長年生産しており、中国のプロの アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカーおよびサプライヤーの 1 つです。バルク梱包を提供する高度で耐久性のある製品を購入すると、迅速な配達で大量の製品を保証します。長年にわたり、お客様にカスタマイズされたサービスを提供してきました。お客様は当社の製品と優れたサービスに満足しています。私たちはあなたの信頼できる長期的なビジネスパートナーになることを心から楽しみにしています!私たちの工場から製品を購入することを歓迎します。