- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
中国 アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカー、サプライヤー、工場
- View as
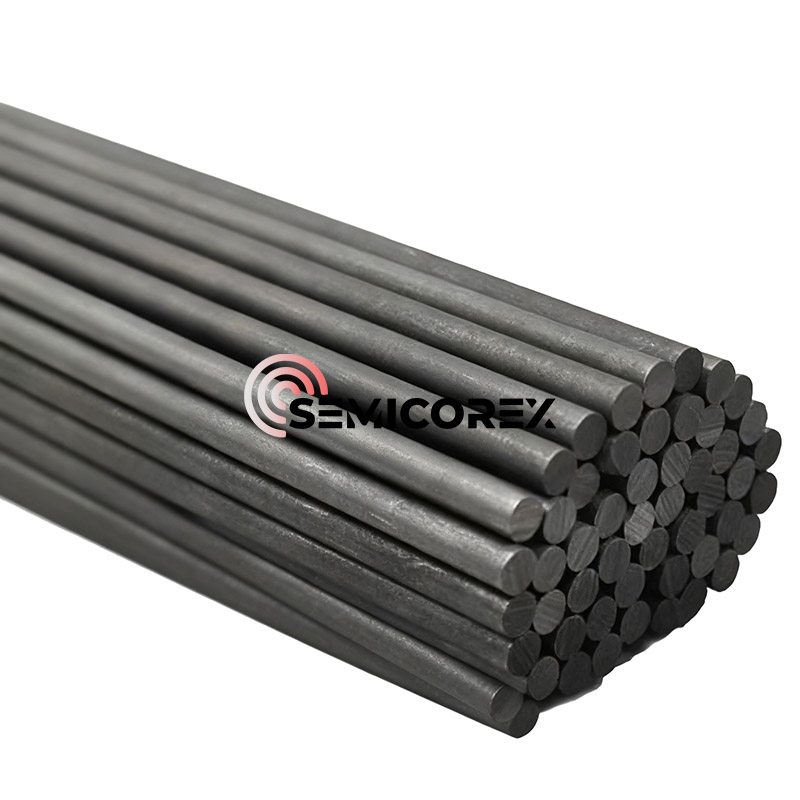
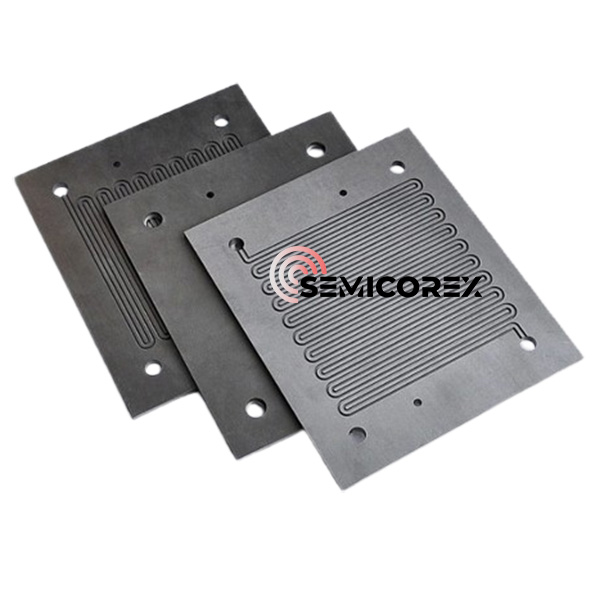
グラファイトバイポーラプレート
Semicorex グラファイト バイポーラ プレートは、現代のエネルギー システムに不可欠なコンポーネントであり、優れた導電性、熱管理、機械的強度の組み合わせを提供します。 PEM 燃料電池やフロー電池へのその応用は、クリーン エネルギー技術の進歩におけるその重要な役割を浮き彫りにしています。
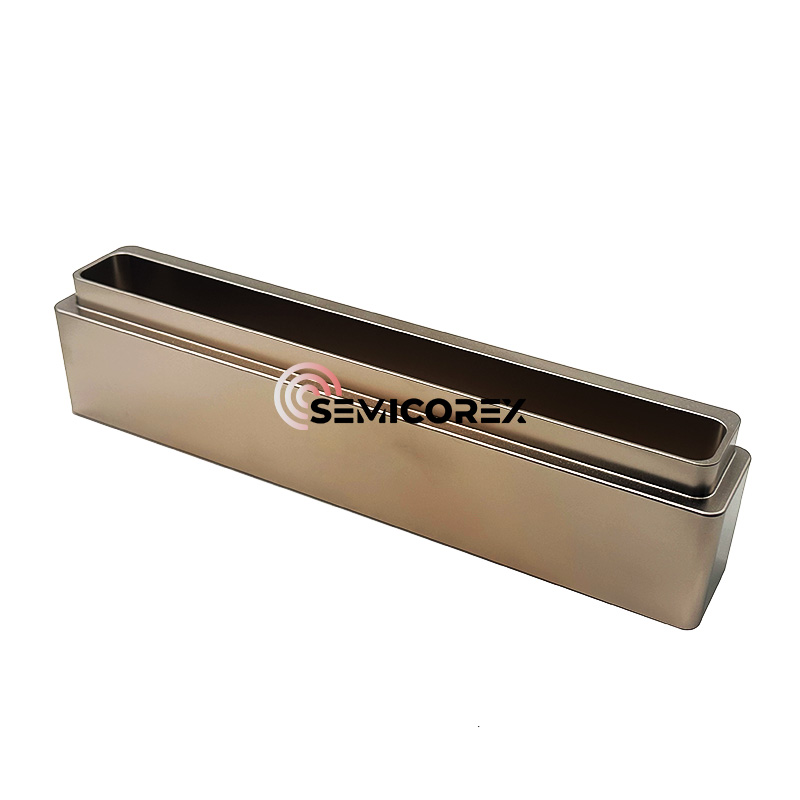
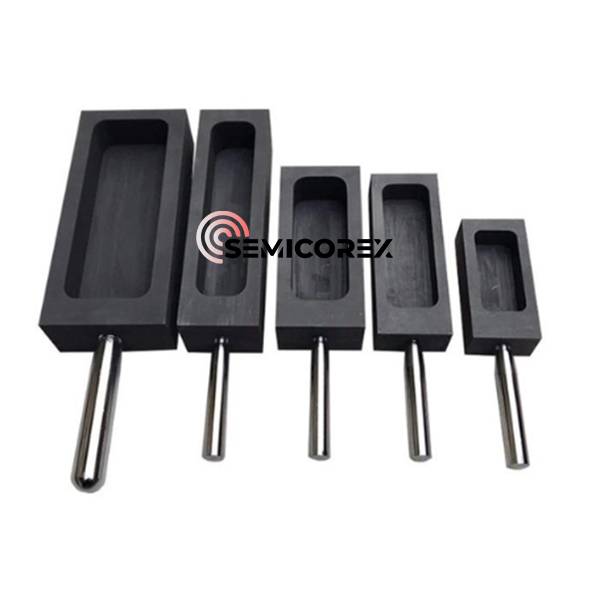
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信精製グラファイトモールド
Semicorex 精製グラファイトモールドは、さまざまな工業用鋳造および成形プロセスにおいて多用途かつ効率的なツールです。高純度、低熱膨張、優れた表面仕上げにより、精度と品質を必要とする用途に最適です。
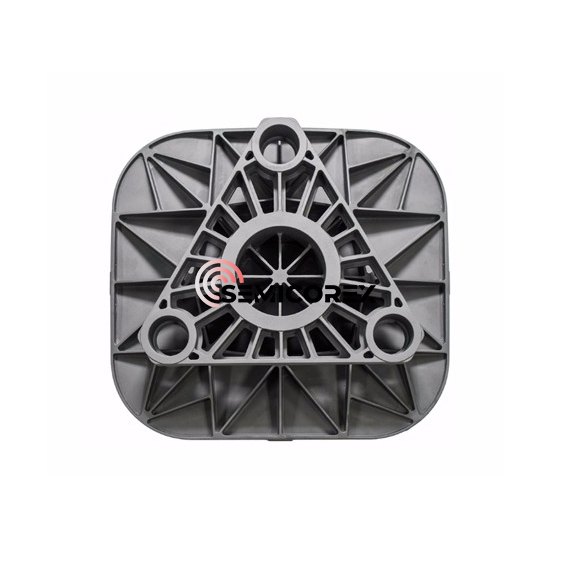
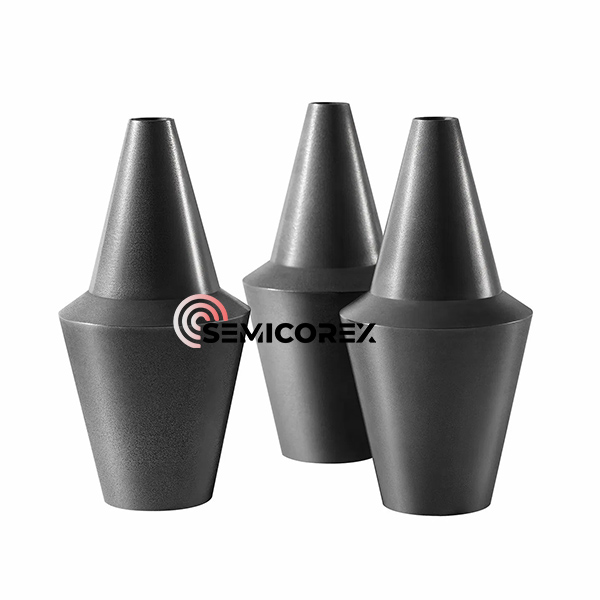
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信グラファイトイオンインプラント
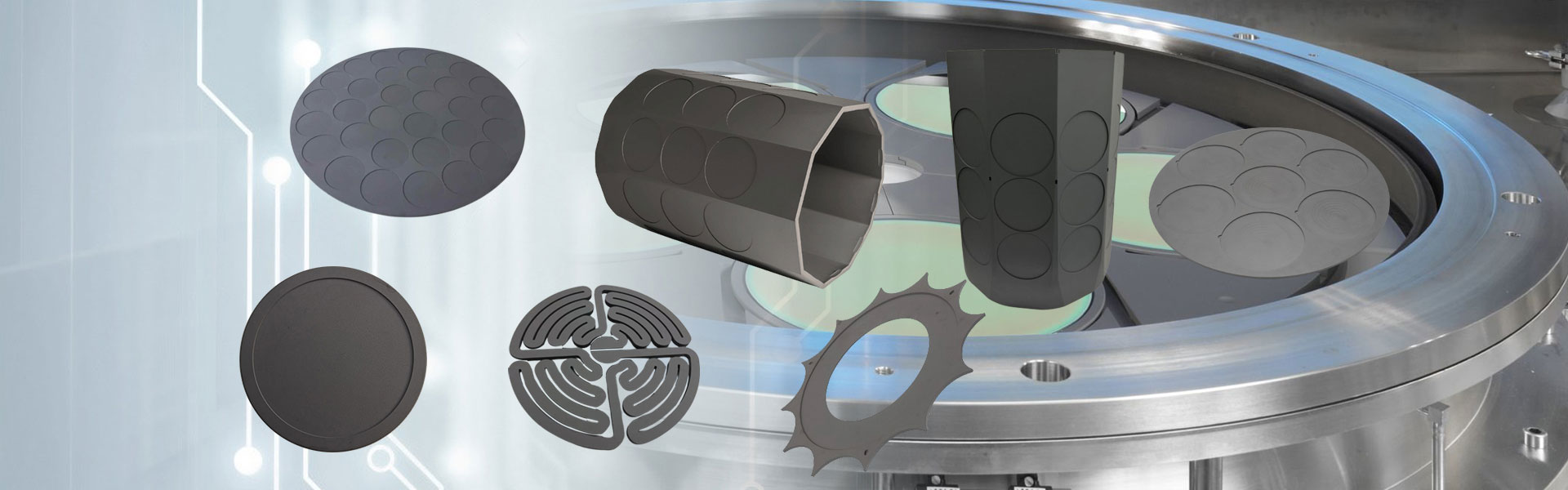
Semicorex グラファイト イオン 注入装置は、微粒子組成、優れた導電性、および極限条件に対する回復力が特徴で、半導体製造の分野で重要なコンポーネントとして機能します。
続きを読むお問い合わせを送信
Semicorex は アイソスタティックグラファイト を長年生産しており、中国のプロの アイソスタティックグラファイト メーカーおよびサプライヤーの 1 つです。バルク梱包を提供する高度で耐久性のある製品を購入すると、迅速な配達で大量の製品を保証します。長年にわたり、お客様にカスタマイズされたサービスを提供してきました。お客様は当社の製品と優れたサービスに満足しています。私たちはあなたの信頼できる長期的なビジネスパートナーになることを心から楽しみにしています!私たちの工場から製品を購入することを歓迎します。